自分が使っているのはM5Stack Core2 for AWSなので、M5Stack Core2+M5GO Bottom2のスタック。
MPU6886はM5GO Bottom2側にあり、軸の向きが分からず動かしながら調べた結果がこれ、よく分かっていないので間違っているかも。
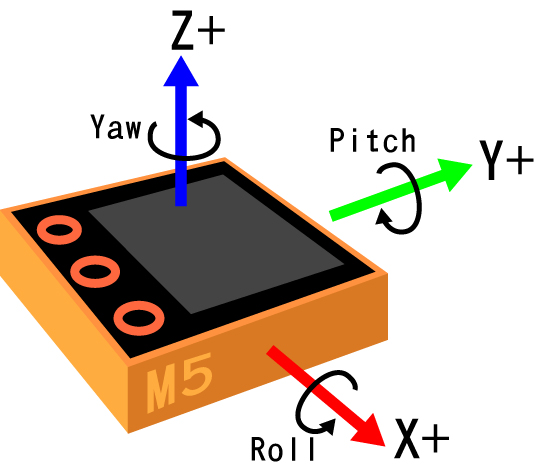
MPU6886:6軸IMUユニットのサンプルプログラム
#include <M5Core2.h>
float accX = 0.0F; // Define variables for storing inertial sensor data
float accY = 0.0F;
float accZ = 0.0F;
float gyroX = 0.0F;
float gyroY = 0.0F;
float gyroZ = 0.0F;
float pitch = 0.0F;
float roll = 0.0F;
float yaw = 0.0F;
float temp = 0.0F;
/* After M5Core2 is started or reset
the program in the setUp () function will be run, and this part will only be run once.
*/
void setup(){
M5.begin(); //Init M5Core.
M5.IMU.Init(); //Init IMU sensor.
M5.Lcd.fillScreen(BLACK); //Set the screen background color to black.
M5.Lcd.setTextColor(GREEN , BLACK); //Sets the foreground color and background color of the displayed text.
M5.Lcd.setTextSize(2); //Set the font size.
}
void loop() {
//Stores the triaxial gyroscope data of the inertial sensor to the relevant variable
M5.IMU.getGyroData(&gyroX,&gyroY,&gyroZ);
M5.IMU.getAccelData(&accX,&accY,&accZ); //Stores the triaxial accelerometer.
M5.IMU.getAhrsData(&pitch,&roll,&yaw); //Stores the inertial sensor attitude.
M5.IMU.getTempData(&temp); //Stores the inertial sensor temperature to temp.
//gyroscope output related.
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 20); //Move the cursor position to (x,y).
M5.Lcd.printf("gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ"); //Screen printingformatted string.
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 42);
M5.Lcd.printf("%6.2f %6.2f%6.2f o/s", gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ);
// Accelerometer output is related
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 70);
M5.Lcd.printf("accX, accY, accZ");
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 92);
M5.Lcd.printf("%5.2f %5.2f %5.2f G", accX, accY, accZ);
// Pose output is related
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 120);
M5.Lcd.printf("pitch, roll, yaw");
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 142);
M5.Lcd.printf("%5.2f %5.2f %5.2f deg", pitch, roll, yaw);
// Inertial sensor temperature output related
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 175);
M5.Lcd.printf("Temperature : %.2f C", temp);
delay(100); // Delay 10ms.
}コードの意味
中味を少しは理解しようと試みたがとても無理、初めのこのコードで挫折。
M5.IMU.getGyroData(&gyroX,&gyroY,&gyroZ);
MPU6886.h
#define MPU6886_ADDRESS 0x68
#define MPU6886_WHOAMI 0x75
#define MPU6886_ACCEL_INTEL_CTRL 0x69
#define MPU6886_SMPLRT_DIV 0x19
#define MPU6886_INT_PIN_CFG 0x37
#define MPU6886_INT_ENABLE 0x38
#define MPU6886_GYRO_XOUT_H 0x43
#define MPU6886_USER_CTRL 0x6A
#define MPU6886_PWR_MGMT_1 0x6B
#define MPU6886_PWR_MGMT_2 0x6C
#define MPU6886_CONFIG 0x1A
#define MPU6886_GYRO_CONFIG 0x1B
#define MPU6886_ACCEL_CONFIG 0x1C
#define MPU6886_ACCEL_CONFIG2 0x1D
#define MPU6886_FIFO_EN 0x23
class MPU688{
public:
enum Ascale {
AFS_2G = 0,
AFS_4G,
AFS_8G,
AFS_16G
};
enum Gscale {
GFS_250DPS = 0,
GFS_500DPS,
GFS_1000DPS,
GFS_2000DPS
};
Gscale Gyscale = GFS_2000DPS; //Gyscale初期値
Ascale Acscale = AFS_8G; //Acscale初期値 ジャイロのフルスケールを選択、GFS_2000DPSが既定値。
gRes = 2000.0/32768.0で、7bitで割ることで基準値gResを算出?
DPS=毎秒度(o/s)、±を考慮して7bit?
MPU6886.cpp
void MPU6886::getGres(){
switch (Gyscale)
{
// Possible gyro scales (and their register bit settings) are:
case GFS_250DPS:
gRes = 250.0/32768.0;
break;
case GFS_500DPS:
gRes = 500.0/32768.0;
break;
case GFS_1000DPS:
gRes = 1000.0/32768.0;
break;
case GFS_2000DPS:
gRes = 2000.0/32768.0;
break;
}
}
void MPU6886::getAres(){
switch (Acscale)
{
// Possible accelerometer scales (and their register bit settings) are:
// 2 Gs (00), 4 Gs (01), 8 Gs (10), and 16 Gs (11).
// Here's a bit of an algorith to calculate DPS/(ADC tick) based on that 2-bit value:
case AFS_2G:
aRes = 2.0/32768.0;
break;
case AFS_4G:
aRes = 4.0/32768.0;
break;
case AFS_8G:
aRes = 8.0/32768.0;
break;
case AFS_16G:
aRes = 16.0/32768.0;
break;
}
}void MPU6886::getGyroData(float* gx, float* gy, float* gz){
int16_t gyroX = 0;
int16_t gyroY = 0;
int16_t gyroZ = 0;
getGyroAdc(&gyroX,&gyroY,&gyroZ);
*gx = (float)gyroX * gRes;
*gy = (float)gyroY * gRes;
*gz = (float)gyroZ * gRes;
}
void MPU6886::getGyroAdc(int16_t* gx, int16_t* gy, int16_t* gz){
uint8_t buf[6];
I2C_Read_NBytes(MPU6886_ADDRESS,MPU6886_GYRO_XOUT_H,6,buf);
*gx=((uint16_t)buf[0]<<8)|buf[1];
*gy=((uint16_t)buf[2]<<8)|buf[3];
*gz=((uint16_t)buf[4]<<8)|buf[5];
} やっていることは、各軸の角速度o/sをジャイロから読んでいるだけ
(1)I2CでMPU6886のMPU6886_GYRO_XOUT_Hレジスタから始まる6バイトを読み込む。
(2)それを2バイトずつHバイト<<8+Lバイトを結合しuint16にする。
(3)更にgResを掛けてジャイロの*gx,*gy,*gzを求め、gyroX,gyroY,gyroZに代入。
(4)加速度も全く同じでM5.IMU.getAccelData(&accX,&accY,&accZ);に変わるだけ。
M5.IMU.getAhrsData(&pitch,&roll,&yaw);
MPU6886.cpp
void MPU6886::getAhrsData(float *pitch,float *roll,float *yaw){
float accX = 0;
float accY = 0;
float accZ = 0;
float gyroX = 0;
float gyroY = 0;
float gyroZ = 0;
getGyroData(&gyroX,&gyroY,&gyroZ);
getAccelData(&accX,&accY,&accZ);
MahonyAHRSupdateIMU(gyroX * DEG_TO_RAD, gyroY * DEG_TO_RAD, gyroZ * DEG_TO_RAD, accX, accY, accZ,pitch,roll,yaw);
}MahonyAHRS.cpp
こちらに至っては手も足もでない、ピッチ、ロール、ヨーの算出をしているようだが、全く分からず諦めることに。
// IMU algorithm update
void MahonyAHRSupdateIMU(float gx, float gy, float gz, float ax, float ay, float az,float *pitch,float *roll,float *yaw) {
float recipNorm;
float halfvx, halfvy, halfvz;
float halfex, halfey, halfez;
float qa, qb, qc;
// Compute feedback only if accelerometer measurement valid (avoids NaN in accelerometer normalisation)
if(!((ax == 0.0f) && (ay == 0.0f) && (az == 0.0f))) {
// Normalise accelerometer measurement
recipNorm = invSqrt(ax * ax + ay * ay + az * az);
ax *= recipNorm;
ay *= recipNorm;
az *= recipNorm;
// Estimated direction of gravity and vector perpendicular to magnetic flux
volatile float q0 = 1.0, q1 = 0.0, q2 = 0.0, q3 = 0.0;
halfvx = q1 * q3 - q0 * q2;
halfvy = q0 * q1 + q2 * q3;
halfvz = q0 * q0 - 0.5f + q3 * q3;
// Error is sum of cross product between estimated and measured direction of gravity
halfex = (ay * halfvz - az * halfvy);
halfey = (az * halfvx - ax * halfvz);
halfez = (ax * halfvy - ay * halfvx);
// Compute and apply integral feedback if enabled
if(twoKi > 0.0f) {
integralFBx += twoKi * halfex * (1.0f / sampleFreq); // integral error scaled by Ki
integralFBy += twoKi * halfey * (1.0f / sampleFreq);
integralFBz += twoKi * halfez * (1.0f / sampleFreq);
gx += integralFBx; // apply integral feedback
gy += integralFBy;
gz += integralFBz;
}
else {
integralFBx = 0.0f; // prevent integral windup
integralFBy = 0.0f;
integralFBz = 0.0f;
}
// Apply proportional feedback
gx += twoKp * halfex;
gy += twoKp * halfey;
gz += twoKp * halfez;
}
// Integrate rate of change of quaternion
gx *= (0.5f * (1.0f / sampleFreq));// pre-multiply common factors
gy *= (0.5f * (1.0f / sampleFreq));
gz *= (0.5f * (1.0f / sampleFreq));
qa = q0;
qb = q1;
qc = q2;
q0 += (-qb * gx - qc * gy - q3 * gz);
q1 += (qa * gx + qc * gz - q3 * gy);
q2 += (qa * gy - qb * gz + q3 * gx);
q3 += (qa * gz + qb * gy - qc * gx);
// Normalise quaternion
recipNorm = invSqrt(q0 * q0 + q1 * q1 + q2 * q2 + q3 * q3);
q0 *= recipNorm;
q1 *= recipNorm;
q2 *= recipNorm;
q3 *= recipNorm;
*pitch = asin(-2 * q1 * q3 + 2 * q0* q2); // pitch
*roll = atan2(2 * q2 * q3 + 2 * q0 * q1, -2 * q1 * q1 - 2 * q2* q2 + 1); // roll
*yaw = atan2(2*(q1*q2 + q0*q3),q0*q0+q1*q1-q2*q2-q3*q3); //yaw
*pitch *= RAD_TO_DEG;
*yaw *= RAD_TO_DEG;
// Declination of SparkFun Electronics (40°05'26.6"N 105°11'05.9"W) is
// 8° 30' E ± 0° 21' (or 8.5°) on 2016-07-19
// - http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag-web/#declination
*yaw -= 8.5;
*roll *= RAD_TO_DEG;
///Serial.printf("%f %f %f \r\n", pitch, roll, yaw);
}M5.IMU.Init()
M5.IMU.Init(); の初期化部分も、訳が分からず途中であきらめた。
regdata = 0x00; //MPU6886_PWR_MGMT_1 パワーマネジメント1レジスタに0x00書き込み
I2C_Write_NBytes(MPU6886_ADDRESS, MPU6886_PWR_MGMT_1, 1, ®data);
delay(10);
regdata = (0x01<<7);//同レジスタに0b10000000書き込み:リセット
I2C_Write_NBytes(MPU6886_ADDRESS, MPU6886_PWR_MGMT_1, 1, ®data);
delay(10);
regdata = (0x01<<0); //クロックAutoSelect
I2C_Write_NBytes(MPU6886_ADDRESS, MPU6886_PWR_MGMT_1, 1, ®data);
delay(10);
regdata = 0x10; //フルスケールを±8gに
I2C_Write_NBytes(MPU6886_ADDRESS, MPU6886_ACCEL_CONFIG, 1, ®data);
delay(1);
regdata = 0x18; //0b00011000 フルスケールを ±2000 dps.
I2C_Write_NBytes(MPU6886_ADDRESS, MPU6886_GYRO_CONFIG, 1, ®data);
delay(1);
regdata = 0x01; //これ以上は分からない
I2C_Write_NBytes(MPU6886_ADDRESS, MPU6886_CONFIG, 1, ®data);
delay(1);MPU-6886データシート p30/59
| ADDR (HEX) | ADDR (DEC.) | REGISTER NAME | SERIAL I/F | BIT7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | 67 | GYRO_XOUT_H | READ | GYRO_XOUT[15:8] |
| 44 | 68 | GYRO_XOUT_L | READ | GYRO_XOUT[7:0] |
| 45 | 69 | GYRO_YOUT_H | READ | GYRO_YOUT[15:8] |
| 46 | 70 | GYRO_YOUT_L | READ | GYRO_YOUT[7:0] |
| 47 | 71 | GYRO_ZOUT_H | READ | GYRO_ZOUT[15:8] |
| 48 | 72 | GYRO_ZOUT_L | READ | GYRO_ZOUT[7:0] |